Perhaps because Interactive Media is still a relatively new programme at NYUAD, a lot of professors and even students are unaware of what IM is – me included. “What exactly is this IM that you are taking?”, asked my ‘Future of Medicine’ professor. “Well, I guess you could say…it’s like…computer science but more hardware?”, I replied. I myself, a current student taking an intro to IM class, did not even know how to explain the subject that I was/am studying. (That’s obviously a fail on my part, so sorry professors if I downplay your subject/discipline, I’m still learning!!) The reading inspired me to create my own definition of IM and right now as it stands, reads: “that sort of media that has digital interactions with people which is basically like when the media interacts with humans by listening, processing and then responding to what was listened and yea…” I’ll need to improve my definition I know, but Crawford told me to make my own definition and that’s mine for now. From now on, I shall work on my explanation of what IM is and hopefully by the end of the semester my definition can improve.
The Jump to Universality – Response
Everything about the reading was going well for me until I reached the part on page 266 where it says that there is “the need for error correction”. The text points to the idea that without the presence of error-correction, all knowledge creation is necessarily bounded. I think I spiraled down into a philosophical rabbit hole after reading this – I thought that it was the opposite. If we don’t have the creation of such thing as right and wrong, shouldn’t our knowledge not be bounded then as there are infinite opportunities to think in any way possible? Wouldn’t error correction be something like manipulating DNA and creating superhumans?!!?
I was stuck in this rabbit hole for a while but decided to accept the idea that was stated on the paper in front of me and continued to read onwards. I realised that the text does explain more about the phenomenon I had just described and I eventually figured out that I was misinterpreting and misreading the whole idea – I had disregarded the fact that this jump to universality and its error correction was in the context of computers. This realisation assured me a lot more because for a good while I was convinced that the author was basically saying that it’s ethical to manipulate DNA, and other theoretically unethical practices.
Overall, I thought it was really interesting for the author to pick out so many examples of the jump to universality in many fields. This reading connected, in many cases, to my other class’ learning about globalisation and how homogeneity and uniformity are influencing and impacting nations, which leads to universality.
The Art of Interactive Design- Response
Reading ‘The Art of Interactive Design’ was an interesting experience. Defining the term ‘interactive’ has always been of interest to me personally due to my research and interest in Interactive Theater. Although Interactive Design is of different nature, much of what I read was coherent and applicable to the ideas I wanted to explore. I liked the use of a ‘conversation’ and the three steps that are claimed to be a criteria for a conversation. Also, I think that the differentiation between interaction and reaction is important. The explicit statement that an interaction is not merely a heightened reaction is important in determining which products can be classified as interactive and which cannot be. The same can be said in regards to participation. The way that different forms of art are considered is helpful in understanding what the author means by interactivity.
The Art of Interactive Design; How is interaction defined?
 In this excerpt from The Art of Interactive Design by Chris Crawford, I disagreed with the base definition of the text: “a cyclic process in which two actors alternately listen, think, and speak.” (Crawford 8) This definition does not take into account that multiple objects can interact at the same time and with each other, as it limits the interaction to only taking place between two “actors.”
In this excerpt from The Art of Interactive Design by Chris Crawford, I disagreed with the base definition of the text: “a cyclic process in which two actors alternately listen, think, and speak.” (Crawford 8) This definition does not take into account that multiple objects can interact at the same time and with each other, as it limits the interaction to only taking place between two “actors.”
For example, when a class and professor are having a discussion, this is not a simple two-person conversation. All the students (who are engaged and participating) are listening both to the points of the professor and the other students, and are building their contributions to the discussion from the participation of others along with their own opinions/thoughts. The conversation is driven by more than two people listening, speaking, and thinking.
This three step definition also excludes various interactions as it is a very human-centric definition. It rules out interactions with pets that cannot speak, and humans interacting with the environment.
Lastly, I found the style in which the text is written hard to take seriously. While it tried to be lighthearted and funny, I did not enjoy the interruption of the text with the author’s email and note from the editor. The author also tended to put in a lot of disclaimers on his opinion, which I found made him less credible. If I am going to publish a book of my opinions and definitions, I will stand by them fully.
Source:
Crawford, Chris. The art of interactive design: a euphonious and illuminating guide to building successful software. No Starch Press, 2003, intro17fall.nyuad.im/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/chapter1_crawford.pdf.
The Jump to Universality – Response
Even though I do not quite understand the connection between this text and our course material, it is a very interesting read.
With gradual improvement of a system, at some point of history, one improvement would make the system “universal”, gives the system ability to cover every possible instance and potential problem.
However, I do not particularly agree with the author on one point regarding the “universality” of language. My first language Chinese is one of the few languages in the world that do not have an alphabet. Yet I believe it is just as “universal” as any other alphabet based language. One of the points the author brought up is that an alphabet can accommodate all potential words in a language and it would help people to pronounce a foreign word. I have not heard of anyone creating a new character in my life, yet new words and concepts are imported into the system everyday. We do this by combining existing concepts together or transliterate a foreign word using characters that have similar sounds. Perhaps in the old times when people did have the need to create new characters. However, I do not see the difference between that and the time when Shakespeare coined a whole bunch of new words for the English language.
The Art of Interactive Design – Response
Almost every time, I can sense the sense of confusion and even a little mistrust when I tell someone I study “Interactive Media”. Then after a brief pause, I always feel obliged to break down the so-called “Interactive Media”: “You know, we make websites, circuits, videos, machines and stuff.” I often explain the “media” part but not quite the “interactive”because I don’t feel that I understand this word well enough myself. This reading certainly gives me a better understanding.
Conversations with someone who actually listens, thinks and speaks are meaningful conversations; Interactions with something that listens, thinks and speaks are “interactive” interactions. It really makes me think when the author states that most movies, games (non-computer), theatre, dancing and reading are not “interactive” but at most intensive “reaction” “participation”. As interactive designers rather than graphic designers, we should not let the form or the media limits our interactive design choices. The cycle of “listen-think-speak” between a human and a machine is the utmost important element in an interactive design.
Code Examples
I’ll put examples we do in class every week up on github here: https://github.com/aaronsherwood/introduction_interactive_media
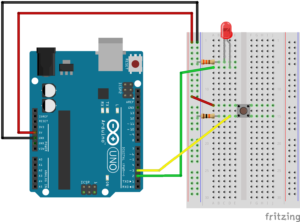
Circuit Diagrams Week 2
Digital Write Circuit (330 ohm resistor by LED)

Digital Write & Read Circuit (10k ohm resistor by button)
There Are No Electrons – Response
In the rather lengthy piece by Ken Amdahl, the concepts of electronics are explained in an interesting and engaging manner. As a novice, I know close to nothing about charges, voltage and resistance. Also, as a more arts driven person the jargon that is presented in textbooks often bore me. Therefore, Amdahl’s work has great value. As the ‘About This Book’ section of the text states, “their minds were alert and engaged by all the fun… therefore receptive to learning anything”. Although long and often ‘dragged’ on, the piece is able to engage its audience and encourages the understanding of concepts rather than memorization. By being able to understand the concepts I believe that one would be able to more effectively work with electronics, no matter the theory one uses to explain it. Thus, the piece is evidently extremely valuable, as well as fun to read.
Assignment 1
While looking through the junk shelf, I found a tennis ball and something that looked like a cardboard cylinder cut down the middle. I had no idea what I wanted to make but I decided to use them as my materials.
At first, I thought I could cut make a cardboard box and balance it on the semi-cylinder so my tennis ball can roll down. But after spending 20 minutes making a cardboard box, I found another (already-made) box-like thing. So I replaced my wonky cardboard box with the sponge box. Then I put copper tape around the tennis ball and on the middle of the slope.

Just as I thought I had finished, I started changing the position of the wire. Others working in the same room told me it looked fine but I decided to spend more time on it by taking everything apart and substituted the copper tape on the box with aluminium foil between and on the box. Later, paper tape was applied to create 3 conducting spots on the box. Lastly, after being unsatisfied with the angle of slope over the weekend, I flipped the semi-cylinder and stuck the box on the other side.

And here is a video of the finished product.
